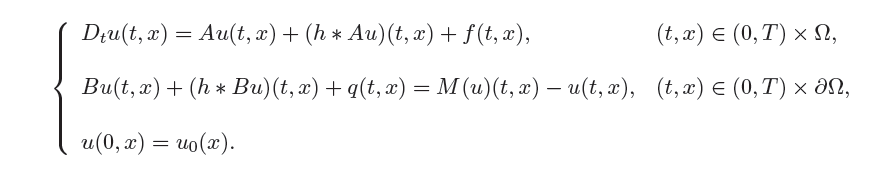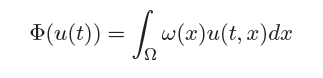MSP 33-37 -New
problems arising in Mathematical Modeling of smart and
biological materials I -II -III -IV -V
The Mini-symposium
is devoted to most recent results concerning
mathematical models, with particular interest in smart
and biological materials.
Notably,
challenging analytical problems are originated from
applications; indeed, new materials are more and more
widely studied since they are used in a variety of
different environments. SpeciŽcally, in recent years
there has been a growing interest, on one hand, in
materials with memory, and smart material in general,
and, on the other hand, in biological materials. Indeed,
all these materials exhibit crucial physical properties;
in the case of materials with memory their behaviour
depends on time not only through the present time but
also through their past history. This peculiarity leads
to the use of such materials in various different
applications, like in biomedical tools and, in general,
in sensors and actuators. Also biological materials
require new analytical instruments to be modeled. More
generally, other problems originating from different
areas of biology as well as of medicine are of interest.
The Minisymposium aims to bring together researchers who
are investigating mathematical problems arising in
modeling of such materials.
Organizers:
Daniele Andreucci
Dipartimento
di Scienze di Base e Applicate per lÕIngegneria
-Sez. Matematica, Sapienza Universit`a di Roma
daniele.andreucci@sbai.uniroma1.it
Sandra
Carillo
Dipartimento
di Scienze di Base e Applicate per lÕIngegneria
-Sez. Matematica, Sapienza Universit`a di Roma
sandra.carillo@sbai.uniroma1.it
Invited Talks
Boundary controllability and source
reconstruction in a viscoelastic string under
external traction
Luciano
PandolŽ
Dipartimento
di Scienze Matematiche, Politecnico di Torino
Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24Ń10129 Torino, Italy
luciano.pandolfi@polito.it
Treatises on
vibrations devote large space to study the
dynamical behavior of an elastic system subject to
known external tractions. In fact, usually a
ŅsystemÓ is not an isolated body but it is part of
a chain of mechanisms which disturb the ŅsystemÓ
for example due to the periodic rotation of
shafts. Ths kind of problem has been rarely
studied in control theory. In the speciŽc case we
shall study, the case of a viscoelastic string,
the effect of such external action is on the
horizontal component of the traction, and so it
affects the coefficients of the corresponding wave
type equation, which will will be time dependent.
The usual methods used in controllability are not
naturally adapted to this case. For example at
Žrst sight it might seem that moment methods can
only be used in case of coefficients which are
constant in time. Instead, we shall see that
moment methods can be extended to study
controllability of a viscoelastic string subject
to external traction and in particular we shall
study a controllability problem which is
encountered in the solution of the inverse problem
consisting in the identiŽcation of a distributed
disturbance source.
Stabilization
for nonlinear integro-differential equations with
weakly singular kernels.
Daniela
Sforza
Dipartimento
SBAI Sezione di Matematica, Sapienza Universit`a
di Roma via Antonio Scarpa, 16 00161 -Roma Italy
sforza@dmmm.uniroma1.it
In this talk
we will show stabilization results for nonlinear
abstract evolution equations in the presence of a
convolution integral term.
For concrete problems, e.g. the motion of
some viscoelastic materials, the effects of the past
time cannot be neglected: in the partial
integro-differential equations describing the motion,
the integral term just represents the memory of the
past.
We will give decay estimates for the
solutions when the convolution kernels are allowed to
be weakly singular functions (integrable functions,
singular at Ót=0Ó) and satisfy sign conditions
consistent with thermodynamical restrictions.
Our main tools are coercive estimates,
properties of positive deŽnite kernels and the
multipliers method: we succeeded in Žnding multipliers
which work even in the presence of integral terms.
Joint work with Piermarco Cannarsa.
Discrete
Observability
Paola Loreti
Dipartimento
SBAI Sezione di Matematica, Sapienza Universit`a
di Roma via Antonio Scarpa, 16 00161 -Roma Italy
loreti@dmmm.uniroma1.it
In the
framework of a classical theorem due to Ingham, we
will discuss some aspects of observability
problems when the observation is given at a Žnite
number of points of the given time.
The talk is based on joint works with Vilmos
Komornik.
Some
existence and uniqueness results in
viscoelasticity: connections with free energies
Sandra
Carillo
Dipartimento
di Scienze di Base e Applicate per lÕIngegneria Š
Sez. Matematica Sapienza Universit`a di Roma, 16,
Via Antonio Scarpa, 00161 Rome, Italy
sandra.carillo@sbai.uniroma1.it or
sandra.carillo@uniroma1.it
Integro-differential model problems arise in
viscoelasticity. Here, some existence, and,
possibly uniqueness, results recently obtained in
joint work with V. Valente and G. Vergara
Caffarelli, in the case, in turn, of a
magneto-viscoelasticity problem [3], [4], or of a
singular viscoelasticity problem [5] are
considered. The connection between analytic
results and the choice of suitable free energies
is pointed out. Furthermore, the problem of the
choice of the free energy, studied in various
different physical models, in joint work with G.
Amendola and A. Manes [1,2], is also considered.
In particular, free energies in viscoelastic
solids and ßuids, [2], are also mentioned
emphasizing their analytical implications as far
as asymptotic behaviour of solutions is concerned.
- Amendola
G., Carillo S. and Manes A. 2010 Classical free
energies of a heat conductor with memory and the
minimum free energy for its discrete spectrum model,
Boll. U. M.l., sect.
B, 421 Š 446 (3) n.ro 3, ISSN: 1972-6724.
- Amendola,
G., Carillo S. and Manes, A. 2012 Free energies for
viscoelastic ßuids. Differential problems and
asymptotic behaviour. preprint;
- Carillo
S., Valente V. and Vergara Caffarelli G. 2011 A
result of existence and uniqueness for an
integro-differential system in
magneto-viscoelasticity, Applicable Analisys: An
International Journal, 1791Š1802, (90) n.ro 12,
ISSN: 0003-6811, doi: 10.1080/00036811003735832
- Carillo
S., Valente V. and Vergara Caffarelli G. 2012 An
existence theorem for the magneto-viscoelastic
problem Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems
Series S. , 435 Š 447 (5) n.ro 3.
doi:10.3934/dcdss.2012.5.435;
- Carillo
S., Valente V. and Vergara Caffarelli G. 2012 A
singular viscoelastic problem: existence and
uniqueness results, submitted.
A phase
transitions model for shape memory polymers
Elena
Bonetti
Universit`a
degli Studi di Pavia via Ferrata 1, 27100 -Pavia
Italy
elena.bonetti@unipv.it
We introduce a new predictive model for
shape memory effects occurring in polymers. In
spite of the great importance such materials have
in new technologies and applications, a very few
mathematical literature have been developed. Shape
memory polymers may be deformed at some
temperature and then recover their original shape
just by thermal actions. This is not so far from
shape memory alloys. However, the process on the
basis of this effect is fairly different (mainly
it is based on some order structure of the
polymers chains), so that a completely new model
has been introduced. Starting from experimental
data we have introduced energy and dissipation
functionals to get constitutive relations Žtting
with experiments. hence, by a generalized version
of the principle of virtual powers we have recover
an evolution PDE system for which we investigate
existence of solutions. This research is developed
in a collaboration with the Research Center on
polymers of Polimeri Europa (ENI).
Free
Energies and Phase Transitions in Materials with
Hysteresis
Alessia
Berti
Universit`a
e-Campus 22060 -Novedrate (CO), Italy
alessia.berti@ing.unibs.it
Claudio
Giorgi
Universit`a
degli Studi di Brescia via Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
claudio.giorgi@ing.unibs.it
Elena Vuk
Universit`a
degli Studi di Brescia via Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
elena.vuk@ing.unibs.it
A
lot of mathematical models for
magnetic hysteresis can be found in the
literature, many of which are exhaustive and Žt
for applications (see, for instance, [1] and [2]).
Unfortunately, none of them is able to describe
the temperature-induced phase transition between
the paramagnetic and the ferromagnetic regime.
Recently, some efforts have been made in order to
apply the Ginzburg-Landau theory in this direction
[3]. In the talk we present a new approach to
paramagnetic-ferromagnetic transition which
involves a suitable order parameter related to the
remnant magnetization. Starting from the skeleton
curve description and exploiting the minimum
(Gibbs) free energy representation, we are able to
highlight the role of the Ginzburg-Landau equation
when phase transitions in materials with
hysteresis are involved. In particular,
applications to ferroßuids and magnetic
shape-memory alloys are expected.
- Atherton
D. L., Jiles D. C. 1986 Theory of ferromagnetic
hysteresis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 61, 48Š60.
- Coleman B. D., Hodgdon M. L. 1986 A constitutive
relation for rate-independent hysteresis in
ferromagnetically soft materials. Internat. J. Eng. Sci. 24,
897Š919.
- Fabrizio M., Giorgi C., Morro A. 2009 Phase transition
in ferromagnetism. Internat.
On a modiŽed
viscous Cahn-Hilliard type system
Gianni
Gilardi
Universit`a
degli Studi di Pavia Strada Nuova 65, 27100 -Pavia
Italy
gianni.gilardi@unipv.it
A system
modelling phase segregation that is similar to the
viscous Cahn-Hilliard system is studied from the
mathematical point of view. The talk regards a
number of results in several directions
(well-posedness, long-time behavior, asymptotic
analysis with respect to a small parameter,
optimal control) that the author recently obtained
in collaboration with P. Colli, J. Sprekels e P.
Podio-Guidugli.
Modelling of
active particles in a mixture of ßuids
Giacomo
Caviglia
Universit`a
degli Studi di Genova, DIMA
via Dodecaneso 35, 16146 -Genova Italy
caviglia@dima.unige.it
Angelo Morro
Universit`a
degli Studi di Genova, DIBRIS via Opera Pia 11a,
16145 -Genova Italy
angelo.morro@unige.it
The motion
of a cell population within an extracellular ßuid
is modelled by viewing cells, ßuid and chemical
attractant (or chemical factor) as constituents of
a mixture. The cells are regarded as active (or
self-propelled) particles. Their geometric
structure is represented by a vector p directed
along a privileged direction of the cells. The
evolution of p is affected by the stretching of
the ßuid and the gradient of the attractant. The
pertinent equations are the continuity equations
for all constituents and the equations of motion
for the ßuid and the attractant. Because of the
active character, the velocity of the cells,
relative to the ßuid, is modelled by a function of
p and of the gradient of the attractant. Relations
with some classical mathematical models of related
biological systems [1-3] are investigated.
- Bellomo, N., De Angelis, E. and Preziosi,
L. 2003 Multiscale modeling and mathematical
problems related to tumor evolution and medical
therapy. J. Theor. Med. 5, 111Š136.
- Hill, N. A. and Pedley, T. J. 2005
Bioconvection. Fluid Dyn. Res. 37, 1Š20.
- Vald«es-Parada, F. J., Porter, M. L.,
Narayanaswamy, K., Ford, R. M. and Wood B.
D. 2009 Upscaling microbial chemotaxis in
porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 32, 1413Š1428.
Modeling
magnetostriction with phase change
Ulisse
Stefanelli
IMATI Š CNR via Ferrata 1, I-27100 Pavia,
Italy
ulisse.stefanelli@imati.cnr.it
I
shall report on some variational
modeling of magnetostrictive effects in solids
[1], especially in shape memory crystals. The idea
is that of ßagging the different phases (that is
the different crystallographic variants) via the
corresponding easy axes of magnetization.
Different modeling regimes will be addressed and
the corresponding existence, approximability, and
control analysis will be outlined [2,3].
This is joint
work with F. Auricchio, A. Reali, A.-L. Bessoud, and
C. Zanini.
- DeSimone,
A. and James, R. D. 2002 A constrained theory of
magnetoelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50,
283Š320.
- Bessoud,
A.-L. and Stefanelli, U. 2011 Magnetic Shape Memory
Alloys: three-dimensional modeling and analysis.
Math. Models Meth. Appl. Sci. 21, 1043Š1069.
- Stefanelli,
U. 2012 Magnetic control of magnetic shape-memory
crystals. Phys. B 407, 1316Š1321.
A Ginzburg-Landau
model in superßuidity
Alessia
Berti
Universit`a e-Campus via Isimbardi, 10 22060
-Novedrate (CO) Italy
alessia.berti@ing.unibs.it
Valeria
Berti
Universit`a degli Studi di Bologna P.zza di Porta
S.Donato, 5 40127 -Bologna Italy
berti@dm.unibo.it
We propose a thermodynamically consistent
model to study the superßuid-normal phase
transition in liquid helium, accounting for
variations of temperature and density. According
to the Ginzburg-Landau theory, the (second order)
phase transition is described by means of an order
parameter, describing the concentration of the
superßuid phase and emphasizing the analogies
between superßuidity and superconductivity. We
decompose the velocity of the ßuid as the sum of a
normal and a superßuid component and we assume
that the normal component is compressible and the
superßuid component satisŽes an evolution equation
similar to the differential equation governing the
motion of the superconducting electrons inside a
superconductor. With these assumptions, the usual
phase diagram of liquid helium is recovered and
the continuity equation leads to a dependence
between density and temperature in agreement with
the experimental data.
Asymptotic
dynamics of nonlinear coupled suspension bridge
equations
Ivana
Bochicchio
Universit`a
degli Studi di Salerno via Ponte Don Melillo,
84084 -Fisciano (SA) Italy
ibochicchio@unisa.it
Claudio
Giorgi
Universit`a
degli Studi di Brescia via D. Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
claudio.giorgi@ing.unibs.it
Elena
Vuk
Universit`a
degli Studi di Brescia via D. Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
elena.vuk@ing.unibs.it
The long-term dynamics of a doubly
nonlinear abstract system is analyzed. In
particular, for a special choice of the nonlinear
terms, the system describes the motion of a
suspension bridge where the road bed and the main
cable are modeled as a nonlinear beam and a
vibrating string, respectively, and their coupling
is carried out by nonlinear springs. The set of
stationary solutions turns out to be nonempty and
bounded in the energy norm. As the external loads
vanish, the null solution of the system is proved
to be exponentially stable provided that the axial
load does not exceed some critical value. Finally,
the existence of a bounded global attractor of
optimal regularity is proved in connection with
quite general nonlinear terms, exploiting a
particular decomposition of the associated
semigroup and bootstrap arguments (see [1], [2]).
- Conti,
M. and Pata, V. 2005 Weakly dissipative semilinear
equations of viscoelasticity. Commun. Pure Appl.
Anal. 4, 705Š720.
- Giorgi,
C., Pata, V. and Vuk, E. 2008 On the extensible
viscoelastic beam. Nonlinearity 21, 713Š733.
Some
qualitative results in the mixtures of
thermoelastic solids
Maria Grazia
Naso
Universit`a
degli Studi di Brescia via Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
naso@ing.unibs.it
In this talk we present a model governing
the thermomechanical deformations for mixtures of
thermoelastic solids. In particular we discuss the
asymptotic behavior of the associated solutions
under suitable assumptions on the constitutive
constants related to the mixtures.
Reconstruction
of a convolution kernel in a parabolic problem
with a memory term in the boundary conditions
Davide
Guidetti
Dipartimento
di Matematica, Universit`a degli Studi di Bologna
Piazza di Porta S. Donato, 5 40126-Bologna Italy
davide.guidetti@unibo.it
We consider a parabolic problem of the
form
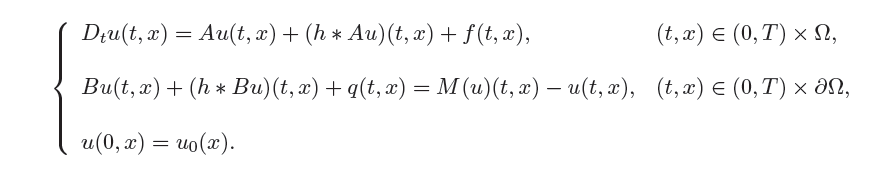
Here A is a linear strongly elliptic
operator of the second order in the open subset ½,
B is a linear operator of the Žrst order, h
is a convolution kernel depending only on t, f, q
and u0 are known data.
M is a nonlinear memory operator, that is, an
operator that, at time t, depends only on the
restriction of u to (0,t) × ½. We
suppose that h is unknown, together with u
and want to reconstruct them. To this aim, we
assume that, for every t the
datum
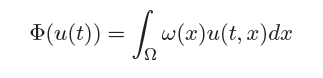
is given. In applications, a problem
of this type is a model of an automatic control
problem, based on a feedback device. We may also
think of h as regulator that we have at
disposal, in order to obtain the prescribed Φ(u(t)).
An
irreversible phase transition problem with a
nonlinear heat ßux law
Giovanna
Bonfanti
Universita`
degli Studi di Brescia via Valotti, 9 25133
-Brescia Italy
bonfanti@ing.unibs.it
We deal with
a phase transition problem characterized by an
irreversible evolution and ruled by a nonlinear
heat ßux law. It is described by the following
system
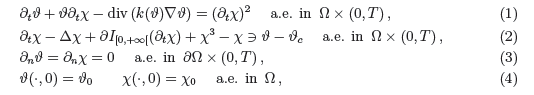
where ½ is a smooth bounded domain in R3 with boundary ¶½, T> 0 is a given Žnal
time, ϑ stands for the absolute temperature, ϑc for the critical
transition temperature, and χ for a phase
variable. Moreover ¶I[0,+°[(į), denoting the
subdifferential of the indicator function
I[0,+°[(į)
(= 0 if the argument is nonnegative, =
+° otherwise), forces ¶tχ
to be nonnegative
and it renders the irreversible
character of the evolution.
Finally, the positive function k,
representing the heat conductivity
of the process, satisŽes suitable
growth conditions and can model
the case of high temperature
phenomena.
The derivation
of (15)-(18) comes from the theory proposed by M. Frmond [2]. The main
analytical difficulty connected with this problem is due
to the presence of the quadratic terms in (15) which
can prevent to deduce global-in-time existence (and
uniqueness) results. Also exploiting the proper
features of the heat ßux law (k is assumed to be
positive and to behave like ϑp ,p ³ 2 for large values of ϑ), we canwork
ina functional setting which is regular enough to
deal with the nonlinearities of the system. We
obtain a global-in-time well-posedness result [1].
- Bonfanti,
G. and Luterotti, F. A well-posedness result for
irreversible phase transitions with a nonlinear heat
ßux law. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. S, in
print.
- Frmond,
M. 2002 Non-smooth Thermomechanics. Springer-Verlag,
Berlin.
These results
have been obtained in collaboration with: Fabio
Luterotti Dipartimento di Matematica, Facolt`a di
Ingegneria, Universit`a di Brescia Via Valotti 9,
25133 Brescia, Italy. luterott@ing.unibs.it
A phase-Želd
model for shape memory alloys at macroscopic
scale: uni-axial deformation tests under different
control conditions
Mirko
Maraldi
DICAM,
Universit`a di Bologna Viale Risorgimento, 2
-40136 Bologna
mirko.maraldi@unibo.it
Luisa Molari
DICAM,
Universit`a di Bologna Viale Risorgimento, 2
-40136 Bologna
luisa.molari@unibo.it
Diego Grandi
Universit`a
di Brescia Via Valotti, 9 25133 -Brescia Italy
diego.grandi@unibo.it
We propose a model for the
thermomechanical behaviour of a shape memory alloy
based on a phase-Želd approach to the underlying
martensitic phase transition [1]. The model is
applied at the macroscopic scale and it is
formulated to capture essentially the
one-dimensional mechanical behaviour; in fact, the
effect of the martensitic phase transition has
been included in terms of a two-variants ruled
uni-axial deformation along a Žxed direction. In
addition to the usual momentum balance equation, a
time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation is
introduced to describe the evolution of the phase;
a central constitutive relation couples the phase
to the deformation. Finally, the heat equation
accounts for the non isothermal effects due to the
phase transformation in a thermodynamically
consistent way. The model has been implemented
within a Žnite-element framework and the
predictions of the mechanical response under
different control conditions are investigated in a
number of numerical tests; the results obtained
are analysed and compared with the experimental
evidences available in literature.
1. D. Grandi, M. Maraldi, L. Molari, A
macroscale phase-Želd model for shape memory alloys
with non-isothermal effects: Inßuence of strain rate
and environmental conditions on the mechanical
response, Acta Materialia 60 (2012) 179Š191.
Diffusion
and current-voltage curves in potassium channels
Daniele
Andreucci, Dario Bellaveglia, Emilio N.M. Cirillo,
Silvia Marconi
Sapienza
Universit`a di Roma Dip. SBAI, via A.Scarpa, 16
00161 -Roma Italy
daniele.andreucci@sbai.uniroma1.it
We consider
the outßux of ions through a ion channel in a cell
membrane. It is well known that such channels
exhibit, among other peculiar features, the
capability of selecting ions of preferred chemical
species, e.g., K+ over Na+ .
The existence of an external voltage
difference across the cell membrane has important
effects on the total current through the channel. We
examine the possibility to predict the behavior of the
current-voltage curves on the basis of a model similar
to the one in [1].
There we introduced a random-walk model
where the channel is lumped to a two state stochastic
point system, and gating of the channel (i.e.,
switching between closed and open phases) is achieved
by means of changes in affinity for the (preferred)
ions, following an idea in [2]. Differently from other
models we take into account also the inßuence of
diffusion in the cell. A mild modiŽcation is needed to
take into account the effect of the trans-membrane
voltage difference.
We shall compare the current-voltage
behavior predicted by our model with experimental
results.
- Andreucci, D., Bellaveglia, D., Cirillo,
E.N.M. and Marconi, S. 2011 Monte Carlo study of
gating and selection in potassium channels. Physical
Review E 84, 021920.
- VanDongen, A.M.J. 2004 K channel gating by
an affinity-switching selectivity Žlter. PNAS 101,
3248-3252.
Two-phase
mass transfer in drug delivery systems: an
application to the drug-eluting stent
Giuseppe
Pontrelli, Andrea Di Mascio
IAC-CNR via
dei Taurini 19, 00185 -Roma, Italy
g.pontrelli, a.dimascio@iac.cnr.it
Filippo de
Monte
DIMEG,
University of LÕAquila via G. Gronchi 18, 67100
-LÕAquila, Italy
filippo.demonte@univaq.it
Biodegradable
polymeric coatings on cardiovascular stents are
commonly used for local delivery of therapeutic
drug to diseased coronary arteries after stenting
procedures. The stent-based drug delivery is not
completely understood and the elution mechanism
may be inßuenced by different concurrent
processes. One of them is the structure of the
arterial wall that is recognized constituted by a
sequence of adjacent layers. The multilayered wall
accounts for a relatively detailed structure for
the macromolecular transport inside the biological
tissues and provides a better description when
compared with a homogeneous monolayered model in
diffusion processes. Another aspect is the porous
coating structure where the drug, initially
present in solid phase, passes into the liquid
phase and, as such, is released in the tissue. We
deŽne a characteristic transfer time and we solve
the transient drug dynamics problem in the
adjoining wall layers faced with the coating. The
endothelium, intima, internal elastic lamina and
media are all treated as homogeneous porous media
and the drug release from the coating through them
is modelled by a set of coupled partial
differential equations. The local non-equilibrium
mass transport in the coating is described by
adding a solid phase equation containing a
solid-ßuid transfer term. A spectral decomposition
method for a multi-layer conŽguration is used.
Drug concentration level and mass proŽles in each
layer at various times are given and discussed. As
long as built on a realistic set up, the current
simulation is able to estimate the local
concentration, offers an easy tool for computing
useful indicators such as the residence time of a
drug and can be used as a guideline for designing
better delivery systems.
Nonlinear
heat transport in nanosystems
Vito Antonio
Cimmelli
Department
of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of
Basilicata, Campus Macchia Romana, 85100, Potenza,
Italy
vito.cimmelli@unibas.it
David Jou
Departament
de F«õsica, Universitat Aut`onoma de Barcelona,
08193 Bellaterra, Catalonia, Spain
david.jou@uab.es
Antonio
Sellitto
Department
of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of
Basilicata, Campus Macchia Romana, 85100, Potenza,
Italy
ant.sellitto@gmail.com
The aim of
this presentation is to analyze some nonlinear
effects arising in heat transport at the
nanoscale, which are especially relevant because,
due to the small size of the heat conductor, small
temperature differences could lead to high values
of temperature gradient.
Such effects are discussed on the basis of a
weakly nonlocal and nonlinear heat transport equation
and a dynamical nonequilibrium temperature [1,2].
Our study will concern not only the
nonlinear effects arising by the dependence of the
thermal conductivity, or of the speciŽc heat, on the
temperature, but also the ones due to terms in the
heat transport equation which are nonlinear in the
heat ßux itself.
The consequences of nonlinearity are
illustrated in different situations of practical
interest, involving nanowires, carbon nanotubes, and
graphene sheets. The thermodynamic aspects are
considered as well.
- V. A. Cimmelli, A. Sellitto and D. Jou,
2010 Nonequilibrium temperatures, heat waves, and
nonlinear heat transport equations, Phys. Rev. B 81,
054301 (9 pages).
- V. A. Cimmelli, A. Sellitto and D. Jou,
2010 Nonlinear evolution and stability of the heat
ßow in nanosystems: Beyond linear phonon
hydrodynamics, Phys. Rev. B 82, 184302 (9 pages).